In today’s digital age, where data breaches and cyber threats loom large, securing online communications has become paramount. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, ensuring that data transmitted over the internet remains confidential and unaltered is crucial. This is where SSL security comes into play. SSL, or Secure Sockets Layer, is a protocol designed to encrypt data and authenticate the identity of websites, providing a secure channel for online interactions.
Enter SSL security—a foundational technology that ensures data privacy, authenticity, and integrity as it traverses the labyrinth of the internet. But what exactly is SSL security, and why should it matter to anyone using the web? This article will unravel the intricacies of SSL, its evolution, implementation, and its invaluable role in safeguarding digital interactions.
SSL Security
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) security is a protocol for establishing authenticated and encrypted links between networked computers. Developed by Netscape in the mid-1990s, SSL was designed to address the growing need for secure internet communication. At its core, SSL security ensures that data sent between users and websites, or between systems, remains private and integral.
SSL operates by using a combination of public and private keys, which encrypt data, making it unreadable to unauthorized entities. When you see a website URL beginning with “https” rather than “http,” it signifies that the site is protected by SSL, adding an extra layer of security for the user.
As the internet expanded, the need for secure communication became more urgent. SSL emerged as the standard for safeguarding sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, personal details, and login credentials, against the prying eyes of cybercriminals.
What is SSL Security?
SSL security, or Secure Sockets Layer security, is a protocol that provides encrypted communication between web browsers and servers. It’s the technology responsible for ensuring that the data exchanged between a website and its visitors remains secure and private. But how does this protocol achieve such a critical task?
The foundation of SSL security lies in its ability to encrypt data. When a user connects to an SSL-secured website, the browser and the server initiate a process known as the SSL handshake. During this handshake, they agree on various parameters for the session, including the encryption methods and the keys used for encryption. This process ensures that any data exchanged is scrambled and only readable by the intended parties.
Beyond encryption, SSL also verifies the identity of the website’s server, instilling confidence in users that they’re communicating with the intended destination and not an impostor. This authentication is crucial, especially in preventing “man-in-the-middle” attacks, where malicious actors intercept and potentially alter communications.
The importance of SSL security is underscored by its widespread adoption across the internet. From banking websites to social media platforms, SSL is present wherever sensitive information is exchanged. Its robust encryption algorithms and authentication processes make it a cornerstone of internet security.SSL has evolved over the years, with the introduction of its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS). While both protocols aim to secure online communications, TLS offers enhanced security features and is the recommended standard today. However, the term “SSL” remains widely used to describe both protocols collectively.
In a world where cyber threats are ever-evolving, SSL security stands as a critical defense mechanism, ensuring that the digital realm is a safer place for all its users.
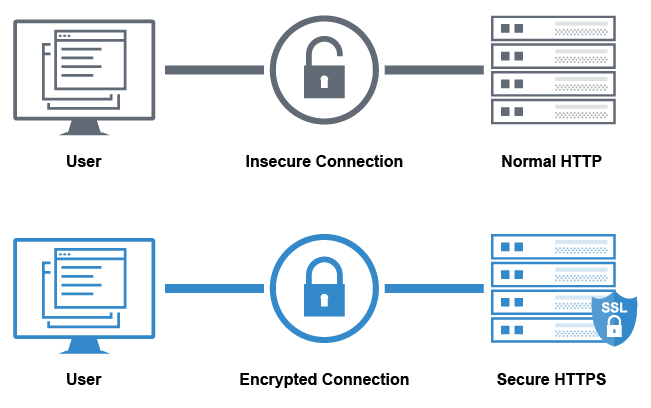
Importance of SSL
Why is SSL security crucial for websites? In a word: trust. In the digital age, trust is the currency that fuels online interactions. Without it, users are hesitant to share information, make purchases, or engage with content. SSL security is the linchpin that fosters this trust.
When users visit a website protected by SSL, they’re greeted with a padlock icon in the address bar. This small symbol represents a significant assurance that their data is encrypted and secure. For businesses, this assurance translates to increased user confidence and potentially higher conversion rates.SSL security is also a critical component of compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These regulations mandate that organizations protect user data, and SSL is a straightforward way to fulfill this requirement.
Beyond compliance and trust, SSL has a direct impact on a website’s search engine rankings. Search engines like Google prioritize secure websites, boosting their visibility in search results. This means that SSL isn’t just a security measure; it’s a competitive advantage in the digital marketplace.In summary, SSL security is indispensable for any website that values user trust, regulatory compliance, and search engine visibility. It’s more than just a technical solution; it’s a strategic asset that enhances the overall user experience.
How SSL Works
The mechanics behind SSL encryption are both fascinating and complex. At its core, SSL relies on a combination of public key and symmetric key encryption to secure data. But what does this mean in practice?
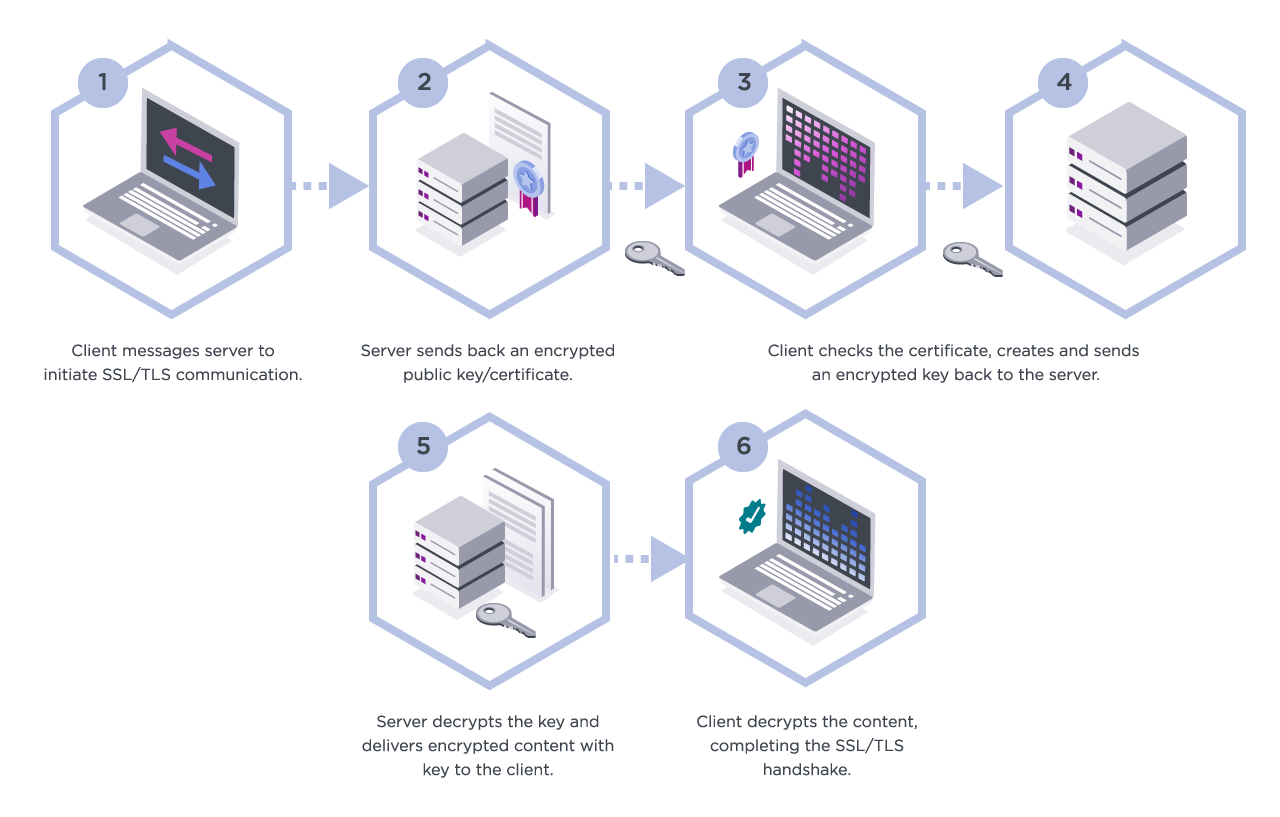
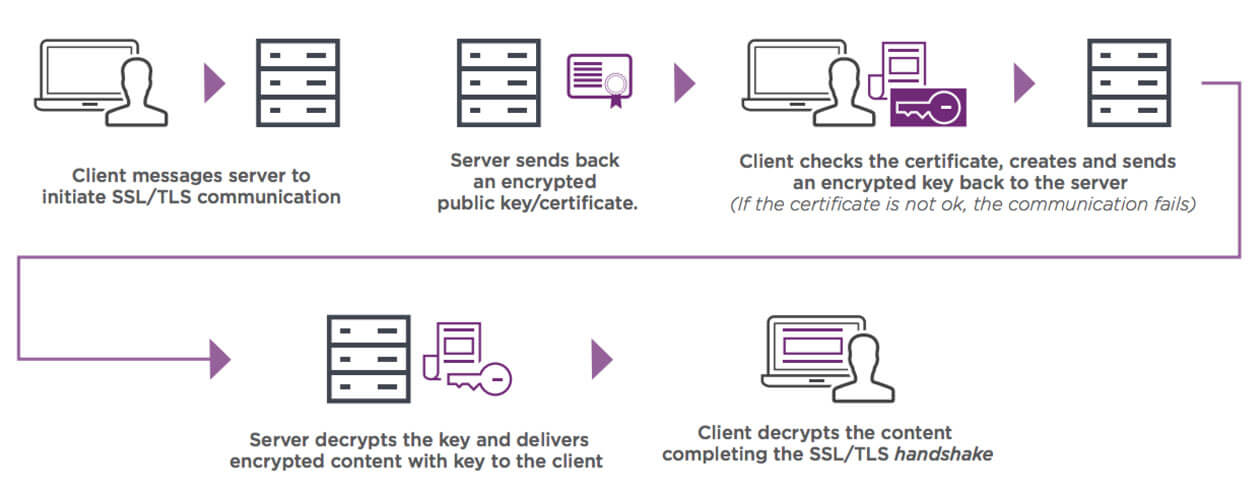
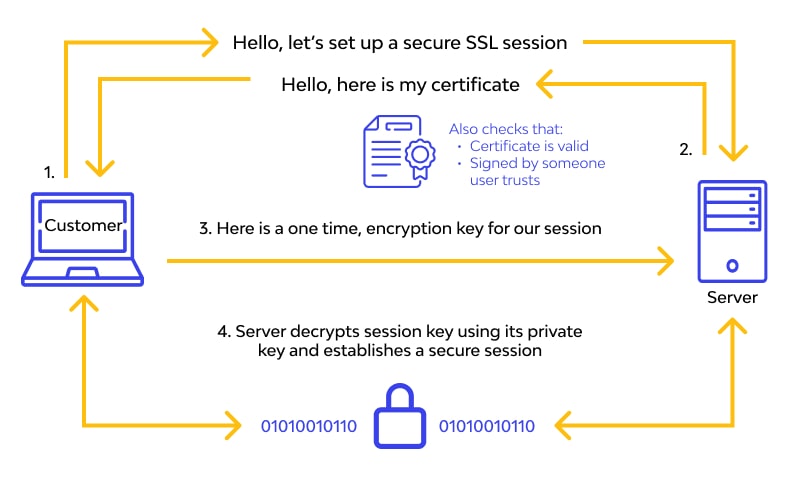
When a user navigates to an SSL-secured website, their browser and the server initiate an SSL handshake. This handshake is a multi-step process that establishes a secure connection between the two parties. Here’s how it unfolds:
- Client Hello: The user’s browser sends a request to the server, proposing encryption methods and generating a random number for the session.
- Server Hello: The server responds with its chosen encryption method, its SSL certificate, and a random number.
- Certificate Verification: The browser verifies the server’s SSL certificate, ensuring it’s issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
- Session Key Creation: Both parties use the exchanged random numbers to create a session key, which is used to encrypt and decrypt data for the duration of the session.
- Secure Connection: With the session key established, the browser and server can securely exchange data.
This combination of public and symmetric key encryption ensures that data remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access. The public key encrypts the data, while the symmetric key allows for efficient decryption.SSL’s intricate encryption process is a testament to its effectiveness in securing online communications. It’s a sophisticated protocol that balances security and performance, providing a safe environment for digital interactions.
Evolution of SSL
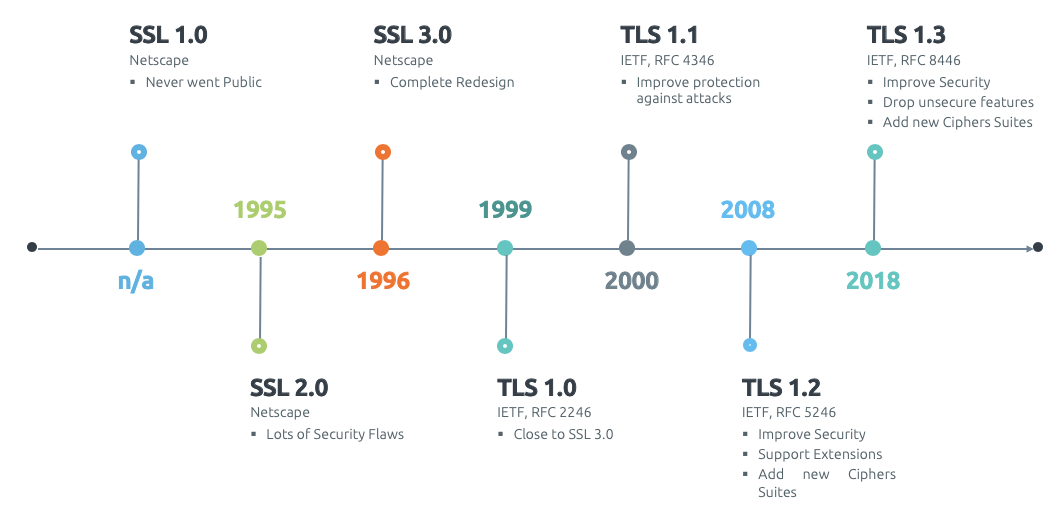
From SSL to TLS: A historical perspective traces the journey of SSL from its inception to its modern-day counterpart, Transport Layer Security (TLS). The story of SSL is one of continuous improvement, driven by the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.SSL was first developed by Netscape in 1995. Its initial version, SSL 2.0, laid the groundwork for secure online communications. However, it was quickly followed by SSL 3.0, which addressed significant vulnerabilities in its predecessor.
As the internet grew, so did the need for even more robust security measures. Enter TLS, introduced in 1999 as an upgraded version of SSL. TLS 1.0 offered enhanced security features and improved performance, making it the preferred protocol for securing internet communications.
Over the years, several iterations of TLS have been released, each building on the strengths of its predecessors. TLS 1.2, for example, introduced support for stronger encryption algorithms and better protection against certain attack vectors.
Today, TLS 1.3 is the latest version, offering significant improvements in both security and speed. It streamlines the handshake process and reduces the number of round trips required to establish a secure connection, resulting in faster, more efficient communications.
The evolution of SSL into TLS reflects the dynamic nature of cybersecurity. As threats continue to evolve, so too must the protocols that protect against them. The transition from SSL to TLS is a testament to the industry’s commitment to ensuring the highest levels of online security.
Types of SSL Certificates
When it comes to SSL certificates, one size doesn’t fit all. Different types of certificates cater to various security needs and levels of authentication. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right SSL solution for a website.
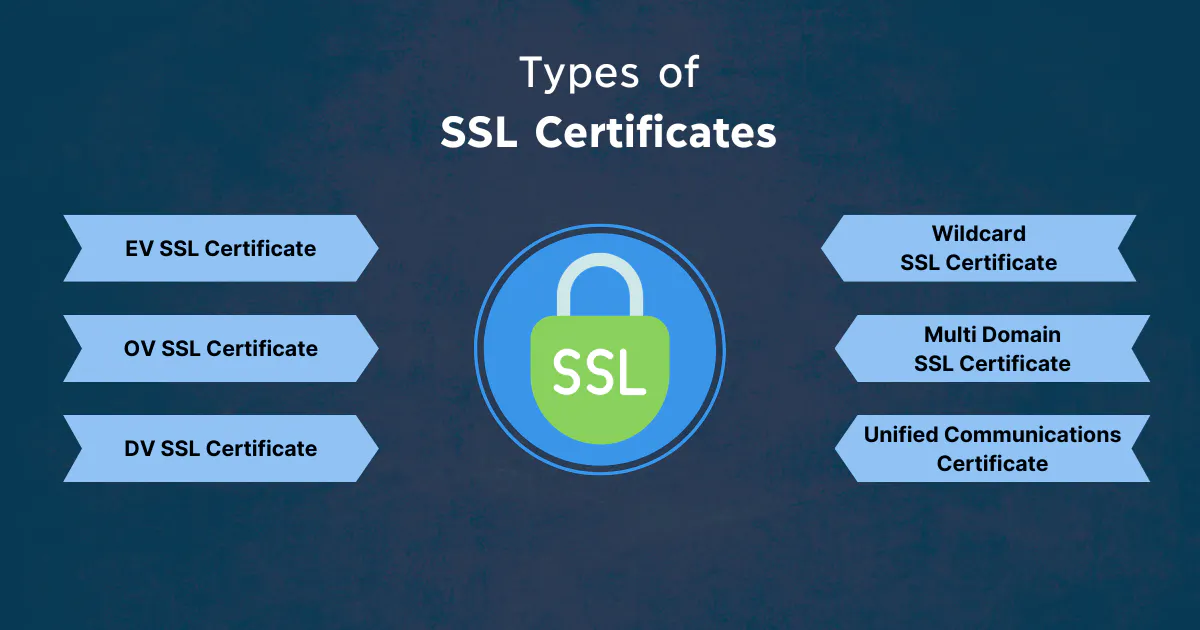
- Domain Validation (DV) Certificates: These certificates offer the most basic level of validation. The Certificate Authority (CA) verifies that the applicant owns the domain. DV certificates are quick to obtain and are suitable for personal websites or blogs.
- Organization Validation (OV) Certificates: OV certificates require a more thorough validation process. The CA verifies the legitimacy of the organization behind the website, providing users with assurance that they’re dealing with a legitimate entity. These certificates are ideal for business websites.
- Extended Validation (EV) Certificates: EV certificates offer the highest level of validation. The CA conducts a rigorous verification process, ensuring the organization’s legal, physical, and operational existence. Websites with EV certificates display a green address bar, instilling maximum trust in users. They’re recommended for e-commerce sites and financial institutions.
- Wildcard Certificates: These certificates secure a domain and all its subdomains with a single certificate. They’re a cost-effective solution for websites with multiple subdomains.
- Multi-Domain (SAN) Certificates: Also known as Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificates, these allow multiple domains to be secured under a single certificate. They’re suitable for organizations managing multiple websites or services, offering flexibility and convenience.
Selecting the appropriate SSL certificate depends on the specific needs of the organization and the level of trust and security required. Whether it’s a personal blog or a multinational corporation, there’s an SSL certificate tailored to fit every requirement.
Obtaining SSL Certificates
Acquiring an SSL certificate is a straightforward yet essential process in establishing a secure online presence. Here’s a step-by-step guide to obtaining an SSL certificate for your website:
- Choose a Certificate Authority (CA): The first step is selecting a reputable CA. These are trusted entities that issue SSL certificates. Some popular CAs include Let’s Encrypt, DigiCert, and Comodo.
- Select the Type of Certificate: Depending on your needs and budget, choose from DV, OV, EV, Wildcard, or Multi-Domain certificates.
- Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR): This is a block of encoded text that you’ll need to provide to the CA. It includes information about your website and your public key.
- Submit the CSR to the CA: The CA will use the CSR to verify your identity and issue the SSL certificate.
- Complete Domain and Organization Validation: Depending on the type of certificate, the CA may require you to prove domain ownership or validate organizational details.
- Receive and Install the Certificate: Once approved, you’ll receive your SSL certificate. You can then install it on your web server.
- Configure Your Server: Ensure your server is configured to use HTTPS, redirecting all HTTP traffic to the secure version of your site.
By following these steps, you can secure your website with an SSL certificate, enhancing trust and protecting user data.
SSL Certificate Authorities
Certificate Authorities (CAs) play a vital role in the SSL ecosystem. They’re the trusted third parties responsible for issuing SSL certificates and vouching for the authenticity of websites. But how do they ensure trust and security?CAs validate the identity of organizations, domains, or individuals applying for SSL certificates. This process involves verifying ownership of the domain and, in some cases, the legitimacy of the organization. By doing so, CAs help prevent fraudulent websites from obtaining SSL certificates and misleading users.
The credibility of a CA is crucial because it directly impacts the trustworthiness of the certificates they issue. Major web browsers and operating systems maintain lists of trusted CAs, ensuring that users can confidently interact with SSL-secured websites.
Popular CAs like Let’s Encrypt offer free SSL certificates, making it accessible for small businesses and individuals to secure their websites. Others, like DigiCert and Comodo, provide a range of certificate types and additional security features, catering to more complex needs.
In essence, CAs are the gatekeepers of online trust, ensuring that SSL certificates are issued responsibly and securely.
Installing SSL Certificates
Once you’ve obtained an SSL certificate, the next step is installation. While the process may vary depending on your web server, the general steps remain consistent:
- Download the SSL Certificate: After issuance, download the SSL certificate files from your CA.
- Install the Certificate on Your Server: Follow your server’s specific instructions. Common servers like Apache, Nginx, and Microsoft IIS have detailed guides available.
- Configure Your Server for HTTPS: Modify your server’s configuration files to enable HTTPS. This often involves specifying the paths to your SSL certificate and private key.
- Test the Configuration: Use online tools like SSL Labs’ SSL Test to ensure your setup is correct and that your site is accessible over HTTPS.
- Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: Implement URL redirects to ensure all traffic is routed through the secure HTTPS protocol.
Installing an SSL certificate might seem technical, but it’s a crucial step in securing your website and building trust with your audience.
SSL and SEO
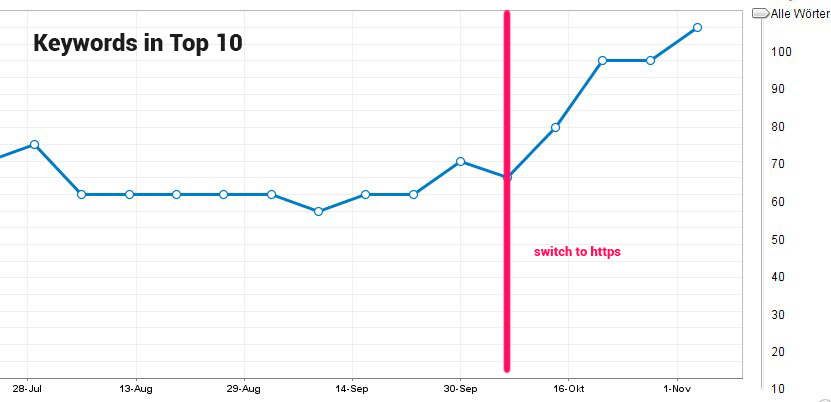
How does SSL impact search engine rankings? The connection between SSL and SEO is more significant than you might think. In 2014, Google announced that HTTPS would be a ranking factor, meaning that secure websites could enjoy a slight boost in search engine visibility.
This move was part of a broader initiative to create a safer internet. With SSL security, websites not only protect user data but also enhance their credibility in the eyes of search engines. As a result, migrating to HTTPS can improve your website’s SEO and potentially increase organic traffic.
Moreover, users are more likely to engage with secure websites. The padlock icon and “https” in the address bar signal trustworthiness, reducing bounce rates and increasing dwell time—factors that search engines consider when ranking websites.
In conclusion, SSL security is a win-win for both security and SEO. Websites that prioritize user safety are rewarded with better search rankings, creating a virtuous cycle of trust and visibility.

SSL for E-commerce
In the world of e-commerce, SSL security is not just an option—it’s a necessity. Online transactions involve the exchange of sensitive information, such as credit card details and personal data, making them prime targets for cybercriminals.SSL security provides the encryption needed to protect this data, ensuring that it remains confidential and secure. For e-commerce businesses, this encryption is critical for maintaining customer trust and preventing data breaches.
Beyond encryption, SSL also authenticates e-commerce websites, assuring customers that they’re dealing with a legitimate business. This authentication is crucial in an industry where fraud and phishing scams are all too common.
E-commerce platforms like Shopify and Magento recognize the importance of SSL security and often include it as part of their service offerings. By securing their websites with SSL, e-commerce businesses can protect their customers, enhance trust, and ultimately drive sales.
Common Misconceptions
Despite its widespread use, there are several common misconceptions about SSL security that persist. Let’s debunk some of these myths:
- SSL is the Same as TLS: While often used interchangeably, SSL and TLS are distinct protocols. TLS is the more secure and modern version of SSL, though the term “SSL” is still commonly used.
- SSL is Only for E-commerce Sites: SSL is beneficial for any website that collects user data, not just e-commerce. Even blogs and informational sites can benefit from the trust and security SSL provides.
- SSL Guarantees Complete Security: While SSL offers robust encryption, it doesn’t protect against all types of cyber threats. It’s just one component of a comprehensive security strategy.
- All SSL Certificates are Created Equal: Different types of SSL certificates offer varying levels of validation and security. It’s essential to choose the right certificate for your needs.
- SSL Slows Down Websites: Modern SSL/TLS implementations are efficient and have minimal impact on website performance.
By understanding these misconceptions, website owners can make informed decisions about implementing SSL security.
SSL and Data Encryption
How does SSL encrypt data? At its core, SSL uses a combination of asymmetric and symmetric encryption to secure data transmissions. This dual approach ensures both confidentiality and efficiency.
During the initial SSL handshake, asymmetric encryption is used to establish a secure connection. This involves the exchange of public and private keys, which are used to encrypt and decrypt data. Once the connection is established, the session transitions to symmetric encryption, using a shared session key for the duration of the session.
Symmetric encryption is faster and more efficient than asymmetric encryption, making it ideal for ongoing data exchanges. It ensures that data remains scrambled and unreadable to anyone intercepting the transmission.
The encryption algorithms used by SSL, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), are designed to withstand modern cryptographic attacks. This level of security is crucial for protecting sensitive information and maintaining user trust.
SSL Vulnerabilities
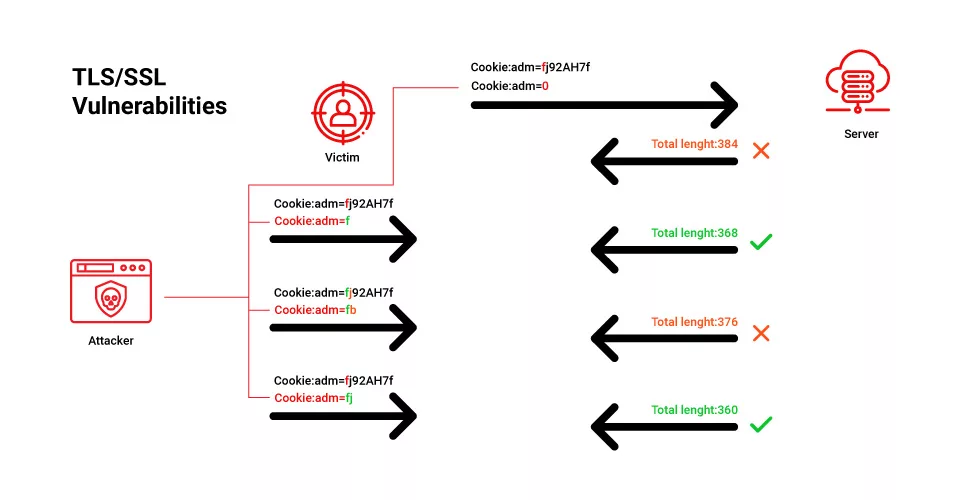
While SSL security is robust, it’s not infallible. Understanding potential vulnerabilities can help website owners take proactive measures to protect their data.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: If a malicious actor intercepts the communication between a user and a server, they can potentially alter or eavesdrop on the data. Implementing strong encryption and regularly updating certificates can mitigate this risk.
- SSL Stripping: This attack downgrades a user’s connection from HTTPS to HTTP, exposing data to potential threats. Enforcing strict HTTPS policies and HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) can prevent SSL stripping.
- Outdated Protocols: Older versions of SSL and TLS are susceptible to various attacks. It’s crucial to use the latest versions and regularly update server configurations.
- Certificate Forgery: If a CA is compromised, attackers can issue fraudulent certificates. Relying on reputable CAs and employing Certificate Transparency can help detect and prevent forgery.
By staying informed about these vulnerabilities, website owners can strengthen their SSL security and protect their users.
Future of SSL
The future of SSL security is an exciting frontier, driven by technological advancements and evolving cyber threats. Emerging trends and innovations promise to enhance the security and efficiency of SSL/TLS protocols.
One such trend is the widespread adoption of TLS 1.3. This latest version offers improved security features, such as encrypted SNI (Server Name Indication) and zero-round-trip time (0-RTT) resumption, which enhances both privacy and performance.
Another promising development is the integration of quantum-resistant algorithms. As quantum computing becomes a reality, SSL/TLS protocols must adapt to protect against potential quantum-based attacks. Researchers are actively exploring cryptographic solutions that can withstand the computational power of quantum computers.
Additionally, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) presents new challenges for SSL security. Ensuring secure communication between a vast array of connected devices requires innovative approaches and scalable solutions.
The future of SSL security is bright, with ongoing efforts to enhance its capabilities and protect against emerging threats. As technology continues to evolve, SSL will remain a cornerstone of internet security, ensuring safe and secure digital interactions.
SSL Security Best Practices
Regular Updates
Keeping software and SSL libraries up-to-date is crucial for maintaining security. Regular updates ensure that any known vulnerabilities are patched, reducing the risk of exploitation.
Strong Encryption Algorithms
Using strong encryption algorithms and key lengths is essential for protecting data. Avoid outdated algorithms, such as MD5 and SHA-1, and opt for more secure options like SHA-256 and AES.
Certificate Management
Proper management of SSL certificates is vital for maintaining security. This includes regularly renewing certificates, monitoring for expiration, and ensuring that certificates are issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs).
SSL and Privacy Laws
Compliance with GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires organizations to implement appropriate security measures to protect personal data. SSL security is a key component of GDPR compliance, as it ensures that data transmitted over the internet is encrypted and secure.
CCPA
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) also mandates the protection of personal data. Implementing SSL security helps organizations comply with CCPA requirements by safeguarding data during transmission and preventing unauthorized access.
Case Studies on SSL Implementation
Success Stories
Several organizations have successfully implemented SSL security to enhance their online security and build customer trust. For example:
- Amazon: The e-commerce giant uses SSL to protect customer data and ensure secure transactions.
- PayPal: The online payment platform relies on SSL to secure financial transactions and protect user information.
Lessons Learned
These case studies highlight the importance of SSL security in protecting sensitive data and maintaining customer trust. Key lessons include the need for regular updates, strong encryption, and proper certificate management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SSL security is a critical component of online communications, providing encryption, authentication, and data integrity. By implementing SSL, organizations can protect sensitive information, build customer trust, and comply with privacy laws. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the importance of SSL security cannot be overstated. Ensuring that your website uses SSL is a vital step in safeguarding your online presence and maintaining the trust of your users.
FAQs about SSL Security
What is SSL security?
SSL security refers to the use of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols to encrypt data transmitted over the internet. This ensures that data remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
How does SSL work?
SSL works by encrypting data transmitted between a user’s browser and a web server. It uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption to secure data and authenticate the identity of websites.
What are the benefits of SSL security?
The benefits of SSL security include data encryption, authentication, and data integrity. SSL ensures that sensitive information remains confidential and protected from eavesdroppers.
What is the difference between SSL and TLS?
TLS is an upgraded version of SSL, offering stronger encryption algorithms and improved security features. While SSL is now considered outdated, TLS is the standard protocol for securing online communications.
How do I implement SSL on my website?
To implement SSL on your website, choose a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), submit the CSR to the CA, install the SSL certificate on your web server, and configure your web server to use HTTPS.
Why is SSL important for e-commerce?
SSL is important for e-commerce because it protects sensitive customer information, such as credit card details and personal data. Implementing SSL helps build trust with customers and ensures secure transactions.
Comment Policy: We truly value your comments and appreciate the time you take to share your thoughts and feedback with us.
Note: Comments that are identified as spam or purely promotional will be removed.
To enhance your commenting experience, consider creating a Gravatar account. By adding an avatar and using the same e-mail here, your comments will feature a unique and recognizable avatar, making it easier for other members to identify you.
Please use a valid e-mail address so you can receive notifications when your comments receive replies.
