Despite launching many attractive advertisements, attractive promotional vouchers…, it still cannot make customers make a purchase. So what is the key point for customers to actually make a purchase? To answer this question, Dr. BJ Fogg – Founder and Director of the Stanford Behavior Design Lab has researched a behavioral model called the Fogg Behavior Model.
Fogg Behavior Model
Fogg’s Behavioral Model was created by American Sociologist BJ Fogg, founder and director of the Stanford Behavior Design Lab. In this model, Fogg pointed out that consumer behavior only changes when three factors occur simultaneously: Motivation, Ability and External Stimulation. If any of these factors are missing, behavior change will not occur.
Specifically, the Fogg Model works as follows:
Behavior (B) = Motivation (M) Ability (A) Trigger(T)
This equation is often shortened to ‘ B=MAT ‘. However, in recent times, ‘Trigger‘ has been changed to ‘Prompt‘. Therefore, you may also see the formula formatted as B=MAP.
This model can be simply understood through the following example:
Suppose we want a user to remember to drink water at the right time of the day. Based on the Fogg model:
-
Motivation: Users want to drink enough water for health, stress reduction and keeping the body healthy.
-
Ability: Drinking water is an easy action that does not require much effort or time.
-
Signal: A health app that sends periodic notifications to remind users to drink water.
Specifically, Fogg described the above details with a graph model below.
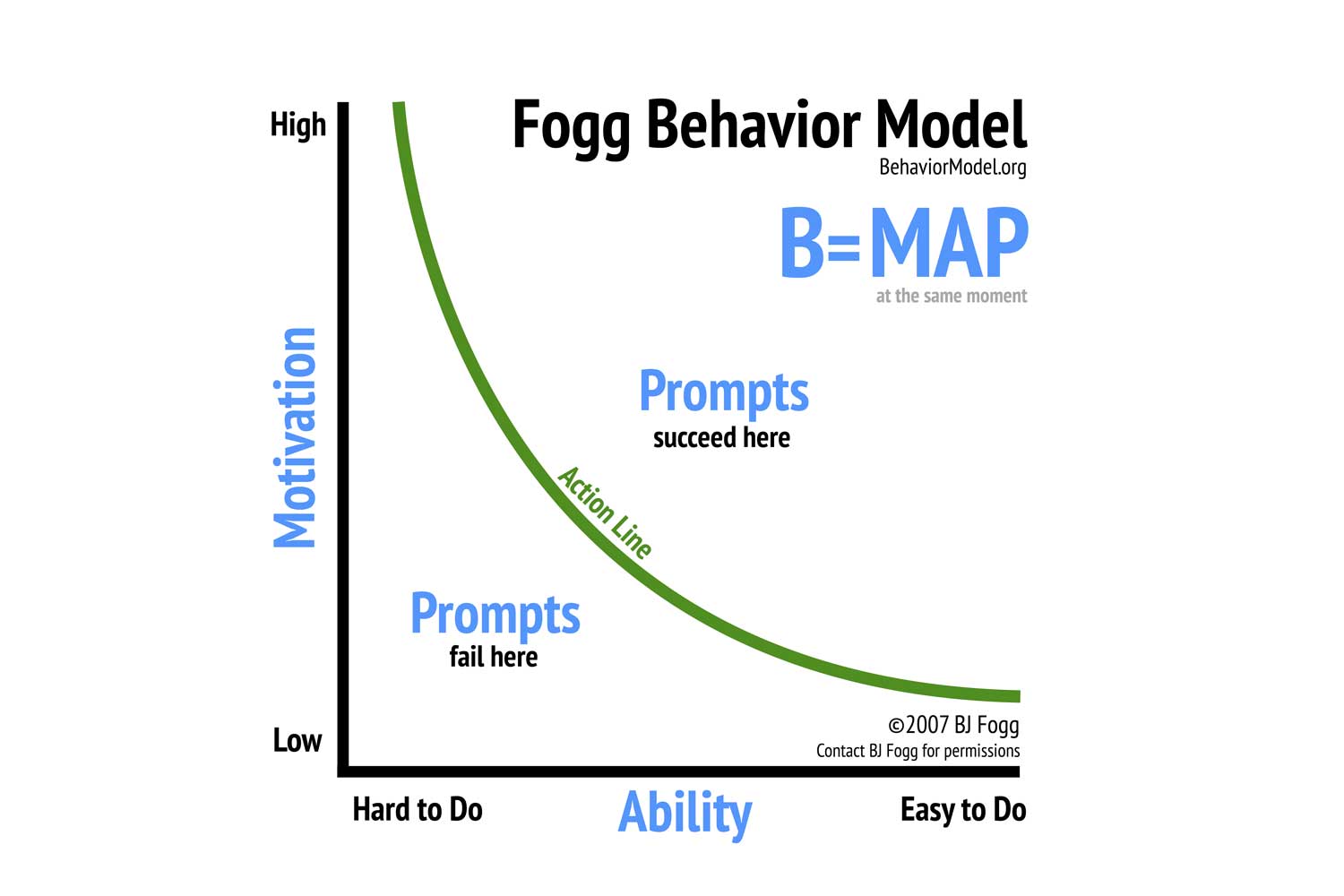
In which, the Action Line axis shows the correlation between motivation and the ability of the person when performing an action. When motivation is low, the ability to perform must be very high to lead to action. On the contrary, when the action is too difficult to perform, the motivation required is very high.
The emergence of the Fogg behavioral model has opened a new chapter in the process of designing products and services and customer approach strategies of brands. Many marketers around the world have used the Fogg behavioral model to design product & marketing strategies, urging customers to perform the actions they desire such as: Purchase, interact with the brand, register, … In addition, more than 1,200 academic publications have referred to this model in the research process. In Marketing, the model
Fogg Model Analysis in Marketing: 3 Factors Driving Customer Behavior
#1. Motivation:
In the Fogg model diagram, the vertical axis represents a person’s level of motivation from low to high. The higher your motivation, the more driven you are to complete the action.
Motivation is a big and very complex concept. However, according to Fogg, we can roughly visualize motivation with three main factors including.
1. Sensation :
Feelings can be physical pleasure or pain that we experience. Humans usually try to avoid pain and strive to achieve pleasure. Therefore, feelings of pleasure will motivate people to continue doing something while feelings of pain will motivate us to stop doing something.
For example, an online fashion app can create a sense of satisfaction for users by using AR, VR technology to allow users to virtually try on clothes right on the website/app: customers can “try on” clothes right on the screen and see how they will look in that outfit. The feeling of satisfaction and fun of trying on clothes without having to go to the store creates a strong motivation, encourages them to explore other products and increases the likelihood of making a purchase.
On the other hand, apps can reduce the frustration of online shopping by offering easy and free returns. Customers don’t worry about “buying the wrong thing” because they know they can return the product conveniently. This makes them feel more comfortable and willing to buy.
2. Anticipation:
Whatever people feel about the future will influence their behavior in the present. Therefore, expectations have the ability to motivate an individual very effectively, through their expectations about the future. In which expectations are divided into two types: hope and fear. Good hopes will motivate them to continue to pursue positive outcomes. On the other hand, when there is a feeling of fear, they will find ways to avoid those negative outcomes.
For example, an online shopping app can motivate users with hope by offering special offers, such as “Shop today and get a free gift or 50% off your next purchase.” The hope of a future reward will make customers quickly make a purchase decision.
Conversely, apps can use fear to motivate customers, by notifying them that a product is “Out of Stock” or “Offer ends in 2 hours.” The fear of missing out on a great deal will motivate customers to act faster to avoid missing out.
3. Belonging:
Attachment is related to social motivations. Humans are social beings. Therefore, we have an innate desire to feel that we “belong” and “fit in” with others in society. Therefore, social acceptance and status are very powerful motivators for their behavior. When an individual feels that they are appreciated and valued, they will tend to promote certain behaviors to increase their acceptance and improve their status.
A simple example of attachment is when a woman sees other girls around her using a certain type of clothing or jewelry, she will be urged to buy more of that product with the desire to fit in like everyone around her. This is also the reason why “Social Proof” is always an indispensable factor in Marketing.
#2. Ability
The horizontal axis of a Fogg figure represents the ability of an individual to perform an action from the difficulty to the ease of performing it. Ability is made up of six elements:
-
Time: Time is always a scarce resource and has the highest opportunity cost. Therefore, according to the Fogg model, the action that the brand wants customers to take must be time-effective. The less time it takes to complete, the higher the probability that customers will take that action.
-
Money: We all make sure to stay within our budget. If a customer can’t afford an action, the likelihood of them taking it is very low.
-
Mental Effort: Thinking is a difficult and tiring task that requires concentration. Therefore, people tend to build habits and choose familiar tasks, acting on an automatic mode in the brain. Therefore, any new behavior that the brand wants to direct customers to should not make their awareness work too much. Customers are more likely to perform a behavior if that behavior does not require them to work too much in terms of thinking.
-
Physical Exertion: We tend to avoid physical exertion unless it actually brings some benefits like releasing endorphins, losing weight, etc. or is a sport they enjoy. So brands need to make the task easier for customers.
-
Social Deviance: People will not like to go against the majority, limit performing behaviors that go against social norms. Therefore, limit asking customers to perform behaviors that go against the general trend of the community. Or if you want them to do it, you must first build a community. That is also the reason why many brands proactively create groups on Facebook, opening up a community space for customers.
-
Habits: Everyone has daily habits. Therefore, it is easier for customers to perform a behavior that is similar to their daily habits.
#3. Activate (or Remind)
Simply put, Triggers are signals, calls to action, etc. that brands can directly influence to motivate consumers to take action, when they have a balance of both motivation and ability. The Fogg model has shown that there are three types of triggers aimed at different groups of people with different levels of motivation and ability:
1. Sparks
Sparks are a type of trigger that is applied when an individual has a high likelihood of performing an action but low motivation . So this type of trigger aims to provide additional motivation to drive their behavior. These triggers should be similar to the user’s previous motivation.
For example: With the customer group of 30-year-old women: The brand has raised the issue of aging in their 30s, encouraging customers to recognize the problem of aging, but they still do not have much real motivation to buy the product because they do not see the effectiveness of the product clearly. At the same time, they also have the ability to pay for the brand’s skin care products.
To help women make a purchase decision, brands can further trigger them with stronger actions such as sending samples with reviews and testimonials from previous customers.
2. Facilitators
Facilitators are a type of stimulus used when the audience is highly motivated but their ability to perform is very low. In this case, the brand needs to provide instructions to help customers perform the action more easily.
For example, in the same case, the brand approaches another group of customers who clearly see aging issues and are eager to use the product. Their finances are enough to buy, but it is still a bit higher than the average spending level, making them hesitate.
In this case, brands can offer buy now pay later programs, allow credit card payments, or offer lower-cost product bundles.
3. Signals
Signals are a type of trigger used when both the user’s motivation and ability are high. These triggers then act as reminders to prompt their actions to happen faster. For example, CTAs in advertising are a type of signal trigger.
Design behavior like you design anything else. Figure out the target behavior, then figure out what needs to change in Motivation, Ability, and Prompting to make it happen. – BJ FOGG
Summary of the 3 elements of the Fogg Behavior Model:
-
-
Motivation: Formed and driven by 3 main factors: Feeling, Expectation and Attachment (Community and social psychology).
-
Ability: Made up of 6 elements: Time, Money, Physical effort, Mental effort, Habit, Deviation from the general view of society.
-
Triggers: Are external stimuli that provide additional motivation, increase performance, or simply notify or remind users, depending on their initial level of motivation and ability.
-
Analysis of Fogg Model through Case Studies of Major Brands
Coca-Cola’s Strategy from the Fogg Model Perspective
It is not possible to conclude with certainty whether Coca-Cola applies this model or not. However, when analyzing the strategy of this brand, it can be seen that the elements that Coca-Cola uses in its marketing activities are very compatible with the Fogg model.
1. Motivation
Coca-Cola motivates consumers by emphasizing the sensory element: the refreshment of drinking cold cans of Coca-Cola, along with the feeling of partying happily with family and loved ones.
-
Sensation: It is not difficult to see that Coca-Cola’s advertisements focus on creating a refreshing feeling when drinking soft drinks, especially when users are thirsty or while resting, or when enjoying them at parties.
-
Anticipation: Through sounds such as opening cans, drinking water, etc., along with images of enjoying Coca-Cola that look very delicious and attractive, along with many attractive dishes, Coca-Cola also stimulates the viewer’s imagination about a cool and refreshing feeling after drinking Coca, thereby encouraging consumers to want to experience this feeling.
-
Belonging: Coca-Cola builds community by associating the brand with elements such as friendship, family and connection. Therefore, it is not difficult to see that this brand always appears during festivals (like Christmas) and Tet. From there, it creates a sense of community and encourages consumers to feel that drinking Coca is like being part of the community, in the festive atmosphere. In addition, Coca-Cola also uses campaigns like “Share a Coke” to create connections between customers.

2. Ability
Coca-Cola makes purchasing and consuming its products very easy through two main factors: price and distribution system:
-
About Price: Coca-Cola has a relatively cheap price, making it easy for every household to access the product.
-
Distribution: Coca-Cola products are available in most convenience stores, vending machines, restaurants and eateries, making it easy for consumers to buy when needed. In addition, the brand also offers a variety of bottle sizes, from individual cans to large bottles of up to 2 liters for large parties.
3. Triggers
Coca-Cola uses a variety of triggers to prompt and encourage purchase behavior.
-
Sparks: Coca-Cola promotes its advertising at times when consumers are most motivated to consume, such as in the summer (the need to quench their thirst) or during festivals (the need to party). Images of people drinking cold Coca-Cola under the hot sun, or clinking glasses of Coca-Cola together at parties, further motivate consumers.
-
Facilitator: Promotions (like buying Coca-Cola and winning prizes) drive stronger purchasing behavior.
-
Signal: The brand is also constantly present, reminding customers through multi-platform advertising campaigns.
How Duolingo Applies the Fogg Model
For service technology platforms like Duolingo, the Fogg behavioral model becomes even more useful. Because it not only attracts users to the platform but also helps maintain their activities on the platform, motivating them to continue to renew in the future. In Duolingo’s strategy, it can be seen that this brand meets the elements of the Fogg model quite well:
1. Motivation
Duolingo motivates users to learn by making the language learning process more fun and engaging:
-
Sensation: With a colorful, easy-to-use interface design, positive sound effects,… combined with humorous, friendly communication strategies on multiple platforms, users feel happy when interacting with Duolingo and want to continue learning.
-
Anticipation: Duolingo stimulates users’ hopes by tracking language proficiency, scores, and streaks. However, the brand also stimulates fears by warning users about the consequences of not learning a language. For example, being criticized at work for not understanding a foreign language, failing an exam because of poor English, etc. Makes learners feel anxious and have to find a way to return to the learning app immediately after.
-
Belonging: Duolingo builds community through leaderboards and language clubs, where users can strive together, share learning tips, and cheer each other on. The brand also thrives on social media, creating a unique culture of the Duolingo community.

2. Ability
Learning a language on Duolingo is quite easy and doesn’t take much of the user’s time:
-
Build learning paths based on users’ input capabilities, helping them not waste time with lessons that are too easy.
-
Lessons are broken down into short sections and chapters, allowing users to learn little by little without feeling overwhelmed. The easy-to-understand and user-friendly interface allows users to learn anytime, anywhere, with just a phone.
3. Triggers
Duolingo regularly uses triggers to remind and encourage users to keep up with their daily learning.
-
Sparks: Many users of online learning apps have the ability to learn but lack motivation. So Duolingo regularly sends reminders or emails with humorous content, such as “The Blue Owl is missing you!”, or sometimes more serious like “You are about to lose your streak”,…
-
Facilitator: Duolingo makes it easier for users to complete lessons by allowing them to study offline on the app, convenient for times when users don’t have an internet connection.
-
Signal: Notifications reminding learners to study and congratulating them on their completion are also continuously sent every day.
Conclusion:
In general, based on the operation of the Fogg Model, brands will clearly understand the factors that influence consumers’ purchasing actions. This model requires brands to carefully research customers’ motivations and capabilities, and consider which factors are lacking. From there, they can build the most effective strategy to approach and promote consumers, avoiding wasting on unnecessary impacts.
Comment Policy: We truly value your comments and appreciate the time you take to share your thoughts and feedback with us.
Note: Comments that are identified as spam or purely promotional will be removed.
To enhance your commenting experience, consider creating a Gravatar account. By adding an avatar and using the same e-mail here, your comments will feature a unique and recognizable avatar, making it easier for other members to identify you.
Please use a valid e-mail address so you can receive notifications when your comments receive replies.