In today’s ever-evolving market, the term Rebranding often pops up in strategic meetings and marketing discussions. But what does it entail, and why are so many businesses considering this path?
Rebranding is a powerful tool that can breathe new life into a business, helping it stay relevant and competitive in an ever-changing market. Whether you’re looking to refresh your brand identity, reposition your brand in the market, or undergo a complete corporate rebranding, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the entire process. From understanding what rebranding is to exploring the steps involved and learning from real-world examples, you’ll gain the insights and knowledge needed to successfully rebrand your business.
Rebranding is more than just a new logo or a catchy slogan; it’s a comprehensive transformation that reflects a company’s mission, vision, and values. This article delves deep into the world of rebranding, offering a complete guide to ensure a successful transition.

What is Rebranding?
Rebranding is the process of changing the corporate image of an organization. It’s a market strategy of giving a new name, symbol, or change in design for an already-established brand. The idea is to develop a new identity in the minds of consumers, investors, and competitors.
While some might think of rebranding as merely a facelift, it is a profound strategic move involving the reassessment of brand identity and brand strategy. A successful rebranding campaign aligns with the company’s core values and communicates them effectively to the target audience. It often involves a Brand Refresh that may include changes in the visual identity, messaging, and even company culture.
Rebranding is a marketing strategy in which a new name, term, symbol, design, concept, or combination thereof is created for an established brand with the intention of developing a new, differentiated identity in the minds of consumers, investors, competitors, and other stakeholders.
When does a Business need to Consider Rebranding?
Rebranding is an important strategic decision and is often made when a business finds it necessary to refresh or adjust its brand to align with current business goals and market trends. Knowing when to rebrand is crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks. Here are some specific cases where a business should consider rebranding:
1. The old brand is no longer suitable for the new direction
When a company changes its vision, mission, or business strategy, the old brand may no longer accurately reflect the company’s new values and goals. To maintain consistency and increase recognition, a rebranding process needs to be done quickly to align the brand with the new direction.
2. Expand or change your target audience
When a business wants to target a new customer group or expand its market, rebranding can help change its brand identity to better suit this new user group. A typical example is Vinamilk’s rebranding campaign in mid-2023 to bring a more dynamic, fresh image, targeting young consumers while still maintaining its core values.
3. Brand is outdated
A brand with an outdated image, logo or message will have difficulty attracting and engaging modern customers. Therefore, rebranding will refresh these elements, helping the brand become more modern and eye-catching.
If your brand looks outdated or no longer resonates with your target audience, it may be time for a refresh.
4. Enhance competitiveness
In the context of today’s fiercely competitive market, rebranding activities can be seen as a strategy to create a difference, attract the attention of customers. This helps businesses maintain or expand market share, enhance brand value and build loyalty from users.

The advantages of successful rebranding for businesses
Step to Rebrand a Business
Businesses can refer to 7 steps to rebranding – The following details can help brands avoid mistakes that can undermine the effectiveness of their strategy:
Research and Analysis
Before starting rebranding, businesses need to conduct research and market analysis to better understand competitors, target customers and current trends. Conduct a thorough assessment of your current brand to identify its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis). This will help you understand the areas that need improvement and set the foundation for your rebranding strategy.
Conduct comprehensive research and analysis to gather insights into your target audience, competitors, and market trends. This will inform your rebranding strategy and ensure it is based on data-driven decisions
Define Rebranding Goals and Objectives
After completing the research, the business needs to clearly define the objectives of the rebranding. This includes identifying what you want to achieve with the rebrand, such as increased brand awareness, market repositioning, or alignment with business goals. Determining clear objectives helps the business focus resources and orient the next activities accurately.
Developing a Rebranding Strategy
Developing a rebranding strategy often involves redefining the core values of your new brand identity, including the name, logo, visual elements, and messaging. Businesses need to clearly define what the key message is that they want to convey and how to do it. This strategy needs to be consistent with the pre-determined rebranding goals as well as reflect the true identity of the business.
Design and Implementation
Once the strategy is determined, the business continues to design new brand elements such as logos, colors, fonts, and other marketing materials. Implementation needs to be done synchronously and consistently across all communication channels, including your website, marketing materials, social media, and customer communications. Ensure consistency and coherence in the new brand identity.
Communication and Promotion
In order for a new brand to spread widely, businesses need to carry out effective communication and promotion campaigns such as using Social Media channels, online and traditional Advertising, PR, etc. suitable for the target customer.

Detailed rebrading process that businesses can refer to
Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitor and evaluate the success of your rebranding efforts by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and gathering feedback from customers and stakeholders. This will help you measure the impact of the rebrand and make any necessary adjustments.
Maintain and Development
Rebranding is not a one-time event but a continuous process, so businesses need to maintain and develop the new brand through improving products, services, and customer experiences. This includes listening to customer feedback, monitoring market trends, and adjusting marketing strategies to ensure the brand is always relevant and attractive to consumers.
Mistakes businesses should avoid when rebranding
Rebranding is a complex, challenging process that requires careful consideration and a clear strategy. Here are some common mistakes businesses should avoid when rebranding:
Lack of market research and analysis
One of the biggest mistakes a business can make is not doing thorough research and analysis before starting a rebranding effort. Not understanding the market, competitors, and target customers can lead to poor decisions.
No clear goals
Unclear or unspecific goals will lead to a vague, ineffective rebranding campaign. Businesses need to clearly define why they need to rebrand and what they want to achieve from this process. Goals may include increasing brand awareness, changing the identity to suit a new customer group, or fixing current brand problems, etc.
Change too much or too little
The right amount of change is an important factor in rebranding. Too much change can cause existing customers to lose recognition or trust in the brand. On the other hand, too little change will not be enough to create the necessary differentiation. Businesses need to find a balance, retaining core elements of the brand while refreshing other elements to attract new customers.

Top common mistakes that cause rebranding campaigns to fall into crisis
Lack of Synchronization in Implementation
Another common mistake is a lack of consistency in the rebranding implementation. This can lead to an inconsistent brand image, confusing customers. Everything from logos, colors, messaging to marketing and communication materials needs to be unified and implemented consistently across all channels.
Failure to conduct effective communication activities
Rebranding is not just about changing the image or logo, but also about informing and explaining these changes to customers. Lack of effective communication will make users not understand the reason and meaning of rebranding, leading to confusion or loss of trust. Businesses need a clear and strong communication strategy to inform and convince customers about these changes.
No Tracking and Evaluation of Results
After implementing a rebranding campaign, it is extremely important to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the campaign. Otherwise, businesses will not know whether the rebranding achieved its goals or whether further adjustments are needed. Businesses should use performance indicators such as brand awareness, Sales, and customer feedback to evaluate effectiveness.
Case Study of Rebranding
Learning from real-world examples can provide valuable insights into the rebranding process. Here are some case studies of successful and failed rebranding efforts.
Successful Rebranding Case Studies of Big Companies
Here are some rebranding case study – The success of major brands has helped businesses make great strides in the market:
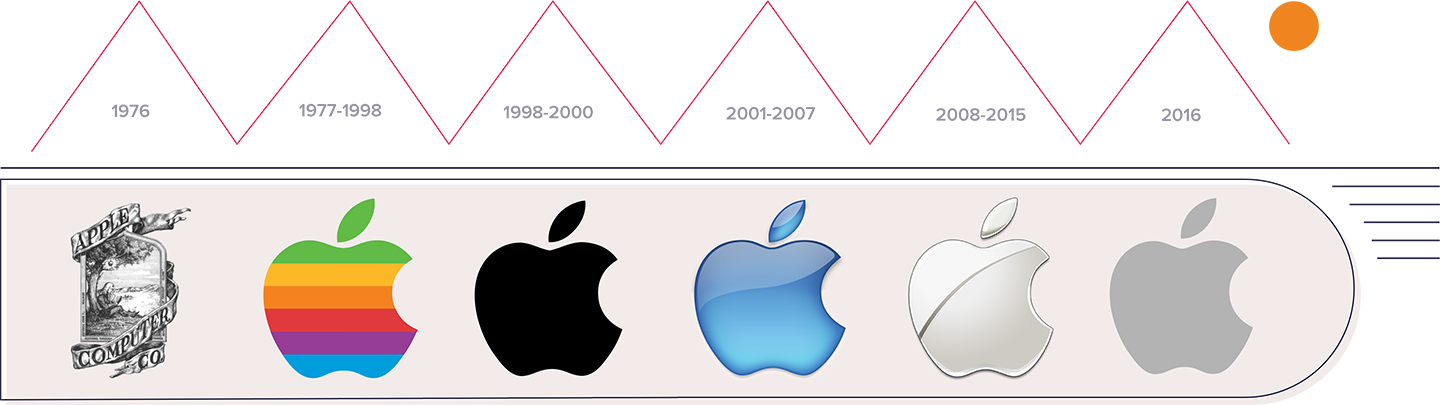
Apple
Apple’s rebranding in the late 1990s, under the leadership of Steve Jobs, transformed the company from a struggling computer manufacturer to a leading innovator in technology and design. The introduction of the iMac, iPod, and iPhone, along with a sleek and modern brand identity, played a crucial role in this transformation.
Old Spices
Old Spice’s rebranding campaign in 2010, featuring humorous and memorable advertisements, successfully repositioned the brand from an outdated product for older men to a trendy and appealing choice for younger consumers

Pepsi
Pepsi is a great example of successful rebranding over the decades. They have rebranded their logo several times to keep up with trends and consumer tastes. Pepsi’s goal is to refresh their image to stay modern and appealing to consumers, while maintaining the youthful and dynamic spirit of the brand. The most recent logo change was in March 2023, when the brand brought a “breakthrough” design compared to the old logo image before.

Pepsi’s latest logo design impresses consumers with its more personality and strength.
Accordingly, the word “PEPSI” is printed in capital letters, surrounded by a circle of three colors: red, blue and white. This giant FMCG group hopes that the combination of blue and electronic black will create a contrast, liveliness, and modernity for Pepsi’s classic colors. In addition, the black color in the new logo also acts as a “growth engine” for the future flagship product line Zero Sugar. Through rebranding, Pepsi not only maintains its competitive position but also increases the love from customers.
7-Up
7-Up is another brand that has successfully rebranded to stay fresh and relevant. Their goal is to refresh their image to appeal to a younger generation of consumers, maintaining their appeal in the competitive beverage market. The 7-Up logo has been simplified, modernized, and incorporated elements that represent freshness, in line with the product’s message of freshness and naturalness. This rebranding helps 7-Up continue to stand firm in the competitive beverage industry.

7-up has made a “renovation” to its brand with a fresher, more youthful identity.
Starbucks
Starbucks is a great example of rebranding when they decided to remove their company name from their logo in 2011. Starbucks’ goal was to simplify their logo to make it more recognizable globally, expand their market, and increase their international presence without being limited by language. They removed the words “Starbucks Coffee” from their logo, keeping only the blue mermaid image. This change made the Starbucks logo more minimalistic and recognizable, reflecting the modernity and globalization of the brand.

Starbucks’ new logo removes text elements, making it easier to remember and recognize.
Lessons Learned from Failed Rebranding Efforts
Tropicana
In 2009, Tropicana’s rebranding effort, which included a new packaging design, was met with significant backlash from consumers. The new design was perceived as generic and unrecognizable, leading to a 20% drop in sales. Tropicana quickly reverted to its original packaging.

Gap
Gap’s 2010 rebranding, which involved changing its iconic logo, was poorly received by customers. The new logo was criticized for being bland and uninspired, leading Gap to revert to its original logo within a week.

Conclude
Rebranding is not an easy process, but when done correctly, it can bring about amazing results that help businesses improve their image, expand their market share and increase profits. Therefore, Investing in rebranding is really necessary for businesses to maintain their competitiveness and develop sustainably in the future.
By understanding the intricacies of rebranding, from brand identity and strategy to execution and measurement, companies can successfully navigate the rebranding process. With careful planning and execution, rebranding can lead to renewed interest, increased market share, and a stronger connection with your audience.
Learning from real-world examples, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can successfully rebrand your business and achieve long-term success. Remember, rebranding is not just about changing your logo or name; it’s about creating a new and compelling brand identity that resonates with your audience and reflects your values.
FAQs for Rebranding
What is rebranding?
Rebranding is the process of changing the corporate image of an organization, including developing a new name, symbol, logo, and related visual assets to create a new and differentiated brand identity.
Why is rebranding important?
Rebranding is important because it can help a business stay relevant, attract new customers, and align with its current vision, mission, and values.
When should a business consider rebranding?
A business should consider rebranding when its brand identity is outdated, market conditions have changed, or the business has grown or evolved.
What are the risks of rebranding?
The risks of rebranding include customer confusion, high costs, and implementation challenges.
How can a business measure the success of rebranding?
A business can measure the success of rebranding by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as brand awareness, customer engagement, sales, and market share, and gathering customer feedback.
What are some common mistakes in rebranding?
Common mistakes in rebranding include lack of research, inconsistent implementation, and ignoring employee input.
How often should a company rebrand?
There’s no fixed timeline, but many companies consider rebranding every 7-10 years to stay relevant.
Can rebranding hurt a business?
If not done carefully, rebranding can confuse customers and dilute brand equity.
How much does rebranding cost?
The cost varies widely depending on the scope and scale of the rebranding effort.
What role do employees play in rebranding?
Employees are brand ambassadors and play a critical role in communicating the new brand identity.
How does rebranding affect customer loyalty?
If executed well, rebranding can strengthen customer loyalty by aligning with their values and preferences.
What’s the difference between rebranding and repositioning?
Rebranding involves changing the brand’s identity, while repositioning focuses on altering the brand’s market position.
Comment Policy: We truly value your comments and appreciate the time you take to share your thoughts and feedback with us. Note: Comments that are identified as spam or purely promotional will be removed. To enhance your commenting experience, consider creating a Gravatar account. By adding an avatar and using the same Email here, your comments will feature a unique and recognizable avatar, making it easier for other members to identify you. Please use a valid email address so you can receive notifications when your comments receive replies.
