The Break-Even Point is a relatively common concept in business and management and is a factor that plays a very important role in assessing the success or failure of a business operation. However, because there are many variables involved, calculating the exact Break-Even Point is still a difficult question for many people. In the article below, let’s learn more about the concept of what the Break-Even Point is and how to determine it accurately.
What is Break-Even Point?
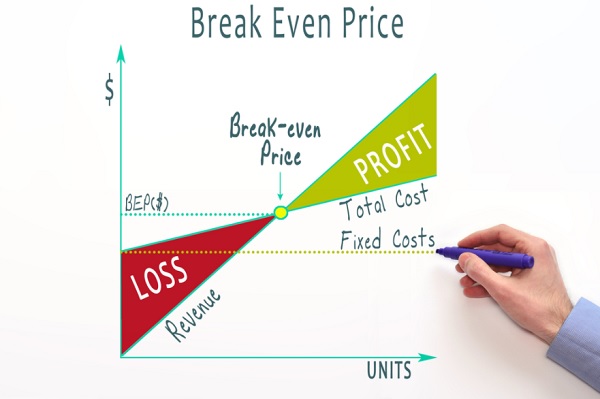
Break-Even Point (BEP) is an important concept in business, accounting and management, used to determine the break-even revenue level that a business needs to achieve to offset all costs. Expenses have been spent, guaranteed not to incur losses and do not include interest.
BEP is the first and prerequisite factor you need to evaluate before deciding to invest in a certain project or business model. Determining the Break-Even Point also helps you accurately plan associated costs, including estimated costs of business management, human resources costs, Advertising costs and a number of other related costs. mandarin.
Break-even point is a factor that helps evaluate the feasibility of business operations
Break-Even Point Classification
Break-Even Point is divided into two main types including economic Break-Even Point and financial break-even point, specifically as follows:
Economic Break-Even Point
The Economic Break-Even Point is the point at which the achieved revenue will be calculated by the total cost of production and business (including fixed and variable costs, not including business loan interest rates) and corporate profit before loan interest. equals 0 and corporate taxes also equal 0.

There are two types of Break-Even Point: Economic Break-Even Point and Financial Break-Even Point
Financial Break-Even Point
Financial Break-Even Point is the point at which revenue will be calculated by total production and business costs, plus business loan interest that needs to be repaid. At the Financial Break-Even Point, the business has neither profit nor loss and its pre-tax profit is now equal to 0.
The Importance of Break-Even Point
It is no coincidence that the Break-Even Point is given such importance in corporate management. This factor greatly determines business efficiency, and is also a premise for building long-term strategies for commercial activities:
It is the premise and basis for building a business plan
One of the important meanings of the Break-Even Point is that it is used to build a business plan. Administrators often use the Break-Even Point to determine the production and Sales output needed to earn the desired profit, and also use this factor to plan other costs such as hiring costs. , advertising costs and selling price construction,….
Accurately evaluate business performance
Break-Even Point in business is also considered a scale to help managers accurately assess the effectiveness of operations. If the Break-Even Point is low, it shows that the business is maximizing its resources and can easily increase its profit margin. On the contrary, if the Break-Even Point is high, the business needs to make adjustments to minimize investment costs.

Break-Even Point helps accurately evaluate business performance
Assess the risks of business activities
Break-Even Point analysis also helps businesses evaluate the risk of business activities. From there, choose to invest in projects with real potential, eliminating projects that are difficult to recover capital and even cause losses.
Break-Even Point Calculation Formula
To accurately determine the Break-Even Point, you can refer to the Break-Even Point calculation formula below:
Break-Even Point (quantity) = Total fixed costs / (Unit selling price – Unit variable cost)
In there:
- Fixed costs: These are costs that do not change with output, such as rent, personnel salaries, network fees, electricity and water, etc.
- Variable costs: These are costs that change proportionally to factors such as output, raw material costs, electricity and water costs used for production.
- Unit selling price: Is the selling price of a product
Break-Even Point calculation example:
Assumption: Suppose a company producing ballpoint pens has fixed costs of 5000 USD/month (factory fee, labor rental); The variable cost for 1 pen is 0.5 USD (price of plastic, metal tip – raw materials, electricity and water,…), the selling price of 1 pen is 1 USD.
From here, the Break-Even Point of that business is determined as follows:
Break-Even Point (number of pens) = 5000 / (1 – 0.5) = 10.000 pens.
However, the Break-Even Point example above only stops at the hypothesis that the business sells a single product. This is not common for businesses at the present time. Most businesses today sell 2 or more products.
How to calculate Break-Even Point
- Step 1: Calculate the ratio of each type of item. The calculation formula is as follows:
- Percentage of each item = (Product revenue/Total business revenue) * 100.
- Step 2: Calculate the average contribution margin percentage. The calculation formula is as follows:
- Average contribution margin percentage = Product contribution margin percentage/Corresponding item ratio of the product.
- Step 3: Calculate the Break-Even Point of the business. The calculation formula is as follows:
- Break-Even Point of the business = Total fixed costs / Average contribution margin ratio.
- Step 4: Calculate the Break-Even Point for each type of product. The calculation formula is as follows:
- Break-Even Point for each item = Enterprise Break-Even Point * Item ratio.
To be able to accurately calculate the Break-Even Point, ensuring it does not deviate too much from reality, you can build separate Break-Even Point calculation excel templates for your business. In particular, it is necessary to divide the sample into 3 main parts: Calculate Break-Even Point, fixed costs and variable costs.

Apply the calculation formula to determine the most accurate break-even point
Notes when analyzing Break-Even Point
As mentioned, the actual Break-Even Point is not fixed and can change from time to time, depending on many variables. Therefore, when calculating and analyzing Break-Even Point, you need to pay special attention to the following points:
- Be sure to accurately determine variable costs and fixed costs, and have a clear division to be able to accurately calculate the Break-Even Point.
- For businesses selling many products, it is necessary to convert to a single product to accurately calculate the Break-Even Point.
- The process of calculating Break-Even Point is more or less misleading because the Break-Even Point calculation formula does not depend on monetary value, so when calculating the Break-Even Point of an investment – business project, you need to pay attention to monetary value at each point in time.
- You should build a Break-Even Point chart to clearly see the direction of the Break-Even Point in each period, thereby setting out appropriate business trends.
Summarize:
Above is information shared about what the Concept of Break-Even Point is and how to calculate Break-Even Point accurately. You can refer to this formula to find the “ideal” Break-Even Point for your business and have the right direction in the future to achieve the results you want.
Comment Policy: We truly value your comments and appreciate the time you take to share your thoughts and feedback with us.
Note: Comments that are identified as spam or purely promotional will be removed.
To enhance your commenting experience, consider creating a Gravatar account. By adding an avatar and using the same e-mail here, your comments will feature a unique and recognizable avatar, making it easier for other members to identify you.
Please use a valid e-mail address so you can receive notifications when your comments receive replies.
